Jawbone deficiency can cause many difficulties in daily chewing and significantly affect aesthetics. Therefore, a sinus lift is considered an optimal solution, creating a solid “foundation” to prepare for successful dental implant placement. Let’s explore detailed information about the sinus augmentation procedure in the article below!
What is a sinus lift?
A sinus augmentation is a dental surgical procedure designed to increase the height and thickness of the upper jawbone. This creates a stable foundation for placing dental implants. Over time, untreated tooth loss can lead to jawbone resorption, which means that the jawbone loses volume and density. This can make implant placement impossible without additional intervention. A sinus lift elevates the sinus floor and restores adequate bone structure, ensuring safer and more predictable outcomes for dental implants.
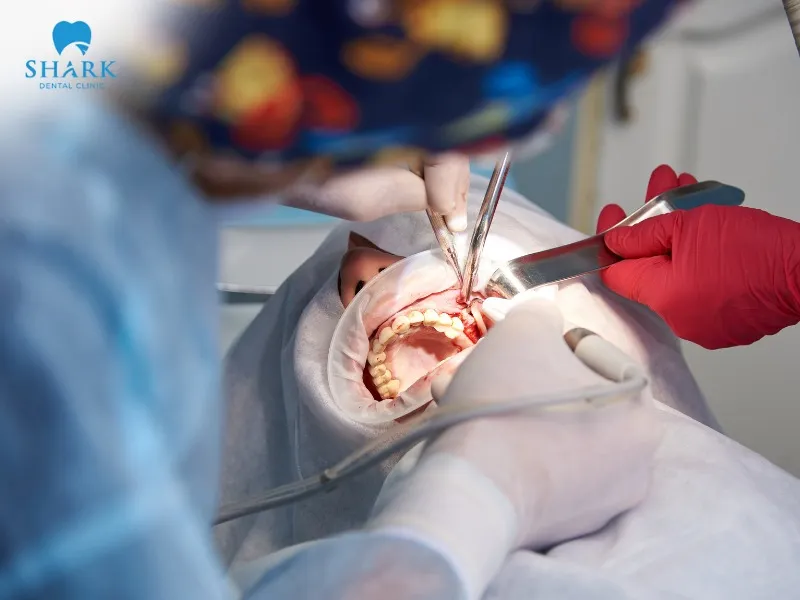
When do you need a sinus lift?
A sinus lift may be recommended in the following situations:
- Long-term tooth loss: Patients who have been missing teeth for an extended period often experience jawbone resorption, resulting in reduced bone height and density. Insufficient or unstable bone makes dental implant placement challenging without a sinus augmentation.
- Thin upper jawbone: A healthy jawbone typically has a thickness of about 8 mm. If the bone is thinner than this, implant placement is not feasible, and a sinus augmentation is necessary to improve bone volume.
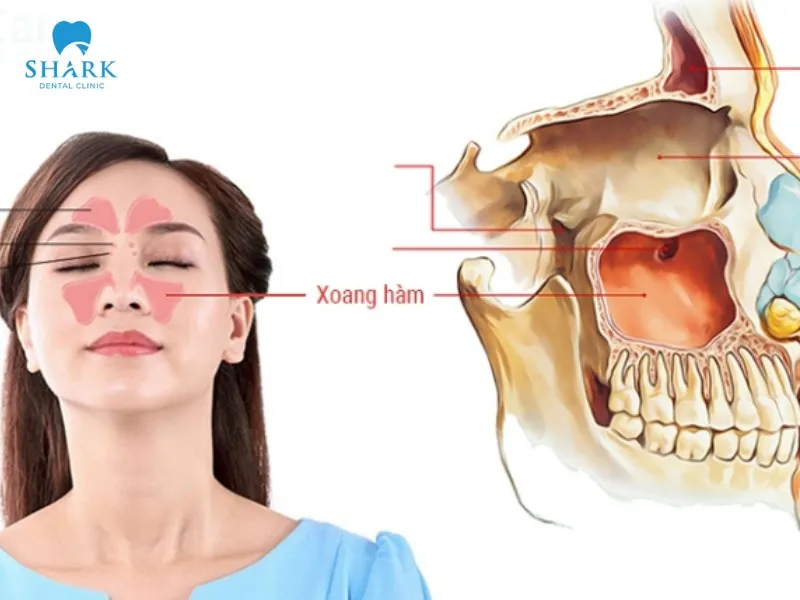
- Low sinus floor position: In many cases, elevating the sinus floor is essential to create a safe distance between the maxillary sinus and the implant fixture. This reduces the risks of complications like bleeding or sinusitis during and after the implant surgery.
A sinus lift should only be performed after a thorough examination and diagnosis by a skilled dentist. Given that this is a relatively complex procedure, it requires precision and experience to ensure patient safety.
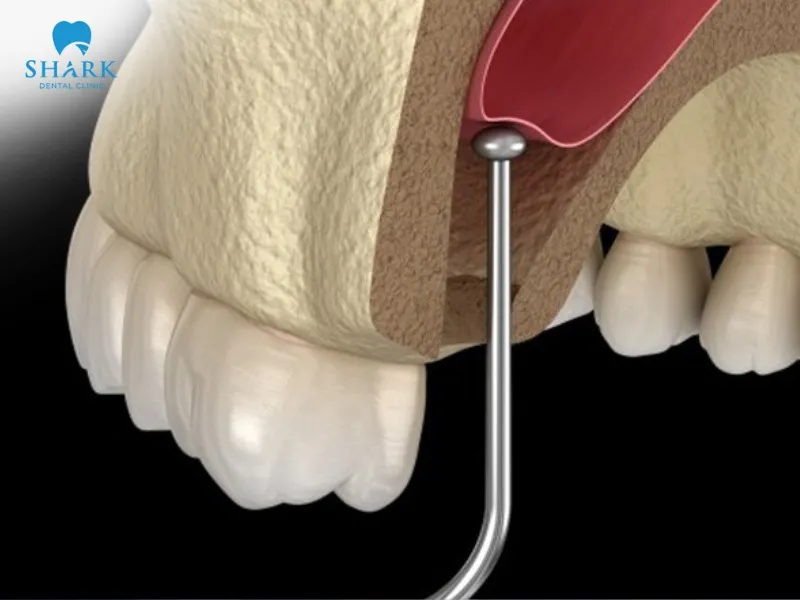
What types of sinus lift procedures are available?
Currently, there are two commonly used sinus augmentation techniques in dentistry: open and closed sinus augmentations.
Closed sinus lift:
A closed sinus lift is performed from inside the oral cavity. The dentist creates a small access point through the gum and bone at the implant site, minimizing soft tissue invasion. Bone graft material—either autogenous (from the patient’s body) or synthetic—is then placed to increase the height and thickness of the jawbone.
This method is typically indicated for patients with mild to moderate bone loss, low sinus expansion, and a smooth sinus floor without fluid accumulation. However, it is suitable only when the sinus membrane is not excessively thick or severely lowered.
Open sinus lift:
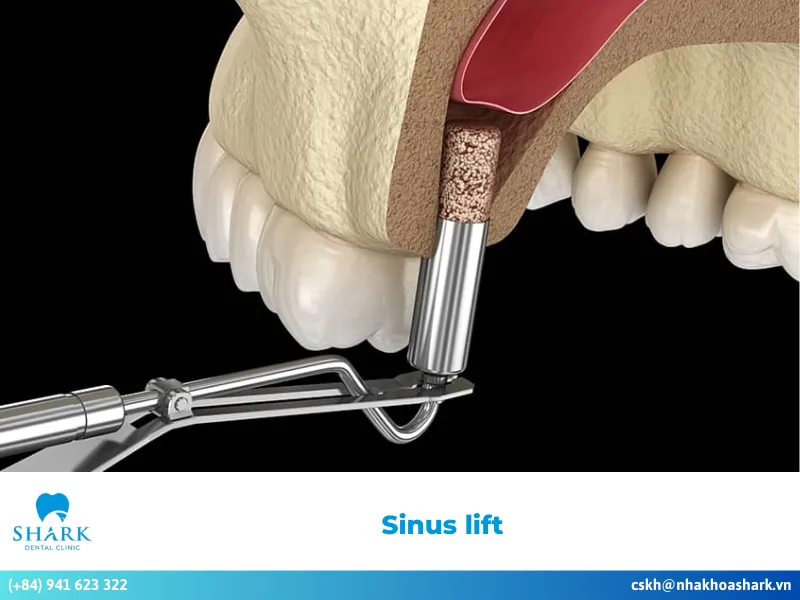
An open sinus lift is performed externally by creating an incision in the gum near the area of the missing tooth. The dentist opens a “lateral window” in the bone to access the sinus cavity and places bone graft material to elevate the sinus floor and significantly increase the jawbone’s thickness.
This approach is appropriate for patients with severe bone loss in the upper jaw, deep sinus cavities, and advanced resorption of the maxillary bone.
How is a sinus lift surgery done?
The procedures for closed and open sinus lifts share some similarities but also differ depending on the clinical case. Specifically:
Closed sinus lift:
Step 1: Examination and Cone Beam CT Scan
The dentist conducts a comprehensive oral examination to assess overall dental health and identify any signs of inflammation or infection. A 3D Cone Beam CT scan is then performed to evaluate the maxillary sinus anatomy, bone thickness, and sinus position, which helps determine the amount of bone graft required.
Step 2: Creating a small access path
Using sterile dental instruments, the dentist makes a small incision beneath the tooth socket. This access point allows the dental tools to reach the sinus floor in preparation for elevation.
Step 3: Performing the closed sinus augmentation
A specialized instrument is gently inserted through the prepared access to carefully elevate the sinus membrane to the pre-calculated height.
Step 4: Bone grafting
Bone graft material—either synthetic or autogenous—is then injected into the elevated space using a delivery tube, creating a solid foundation for future dental implant placement.
Open sinus lift:
Step 1: Examination and 3D CT scan
To begin an open sinus lift, a dentist conducts a thorough examination and orders a 3D CT scan. This allows for an accurate assessment of the jawbone, the degree of sinus pneumatization, the sinus floor, and any presence of sinus fluid.
Step 2: Gum incision
The dentist makes a square or circular incision in the gum near the area of the missing tooth, then gently reflects the mucosal flap to expose the bone surface that requires grafting.
Step 3: Elevation of the sinus membrane
Using sterilized dental instruments, the dentist carefully separates and lifts the sinus membrane, stabilizing it in the appropriate position to prepare for the bone grafting.
Step 4: Bone grafting
Autogenous bone (bone taken from the patient’s own body) or artificial bone material is placed beneath the sinus membrane. The graft is positioned and adjusted to create a solid foundation for future implant placement.
Step 5: Suturing the mucosa
After the grafting, the mucosa is sutured to promote proper wound healing. The patient will then schedule follow-up visits for the dentist to monitor oral healing and recovery.

Cost of a sinus lift
The estimated cost for an open sinus augmentation is approximately 10,000,000 VND, while a closed sinus lift costs around 5,000,000 VND. The cost of artificial bone grafting typically ranges from 4,000,000 VND to 8,000,000 VND. These prices may vary depending on the patient’s condition and the dental clinic performing the procedure.
What are the risks of a sinus lift?
During a sinus lift, patients may encounter certain risks, including:
- Perforation of the Maxillary Sinus Membrane: The membrane lining the sinus cavity may tear during sinus elevation or soft tissue separation.
- Infection and sinusitis: After the procedure, improper oral care may allow bacteria to invade the surgical site, leading to infection. In more severe cases, acute sinusitis may develop.
- Bleeding: Some patients may experience nerve damage during the sinus lift, resulting in excessive or dangerous bleeding.

What’s the recovery like after a sinus augmentation?
The recovery process typically occurs in stages:
- First 2–3 days: Mild swelling of the cheeks and soft tissues may occur, along with slight bleeding at the surgical site. This is a normal healing response and is generally not concerning.
- After 7–10 days: Soft tissues will begin healing, with no pain, bleeding, or uncomfortable tooth sensitivity. At this stage, eating and daily activities become much more comfortable.
- After 4–9 months: This period is necessary for the bone graft material to fully integrate with the jawbone. Patients should maintain a proper diet and attend follow-up appointments as scheduled by their dentist.

What kind of bone is used in a sinus lift?
Various types of bone materials may be used during a sinus lift surgery:
- Autogenous bone: Bone harvested from the patient’s own body, such as from the hip or another part of the jaw.
- Allograft and xenograft bone: Allograft bone is obtained from another human donor, while xenograft bone comes from animals and is thoroughly sterilized.
- Synthetic bone: Artificial bone materials manufactured from calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite, mimicking the structure of natural human bone.
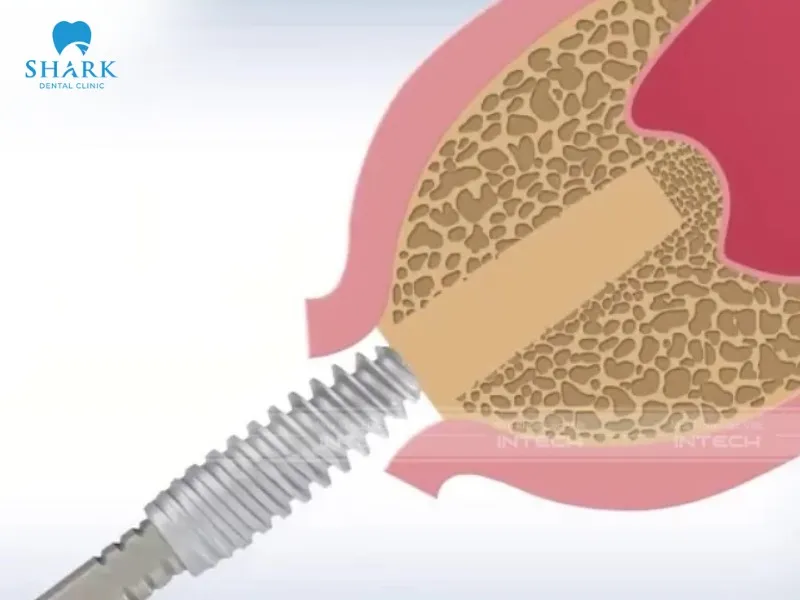
In summary, a sinus augmentation is a crucial procedure that creates a strong foundation for successful dental implant placement, enhancing restorative outcomes. This article aims to provide clearer insight into sinus lift procedures, helping you make an informed decision for achieving a strong, healthy smile.




















Comment on the post