Nowadays, breast augmentation has gradually become a popular cosmetic service for many women, aiming to enhance their attractiveness. Like other surgical procedures, breast augmentation carries certain risks. In this article, we explore the potential breast augmentation risks and ways to minimize complications, helping you prepare both physically and mentally and to make the safest choice for yourself.
Is breast augmentation dangerous?
Breast augmentation is considered a safe procedure when performed at reputable clinics by experienced doctors following strict sterilization protocols. However, risks can still occur due to individual physiology or the quality of the implants.
Complications can range from mild and easily managed to severe, requiring surgery or specialized medical care. Therefore, it is essential for patients to understand potential risks beforehand to be well-prepared in case any complications arise.
>>> See more: How long after breast augmentation can i drive?
Possible risks of breast augmentation
Understanding the details of breast implant surgery is very important, helping patients make informed decisions before undergoing the procedure. Below are the breast augmentation risks that patients should carefully review, including:
Capsular contracture
After breast implants are placed, the body naturally forms a layer of scar tissue around the implant to protect itself from a foreign object. However, in some cases, this tissue can become excessively thick and contract abnormally, pressing on the implant. This can cause the breast to feel firm, appear misshapen, or sit higher on the chest.
Capsular contracture occurs in approximately 10% of patients and can range in severity from mild to severe, classified from Grade I to Grade IV.
Rippling
Rippling occurs when wrinkles or folds of the implant are visible through the skin. While this does not affect the patient’s health, it is considered an aesthetic complication, especially for those with thin breast tissue or when the implant is placed too shallow.
Choosing an appropriately sized implant and placing it under the muscle can help reduce this risk. Consulting with the surgeon beforehand ensures the procedure achieves the best possible aesthetic result.
Implant displacement
Implant displacement can occur if the procedure is performed by an inexperienced surgeon or if the patient engages in vigorous activity before the incision heals. Over time, the breast implant may shift from its original position, causing asymmetry or uneven breasts. This is also referred to as malpositioned implants, and if necessary, the patient may require corrective surgery to reposition the implant.
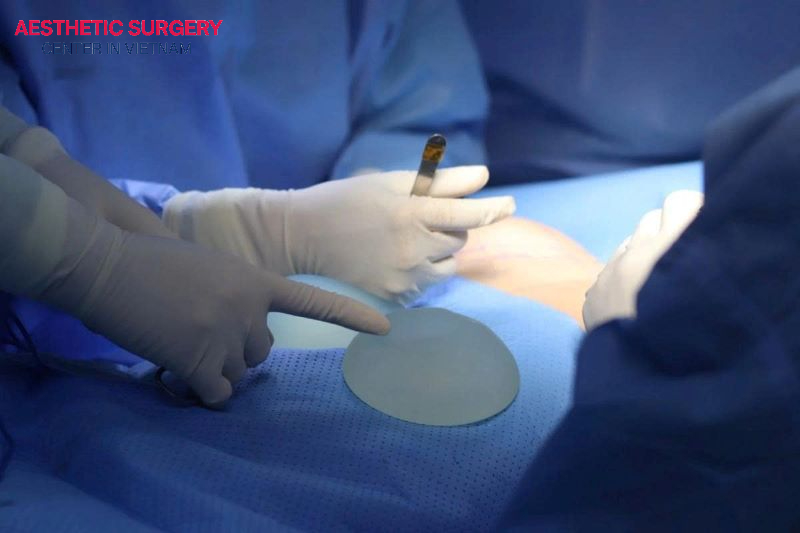
Breast implant rupture
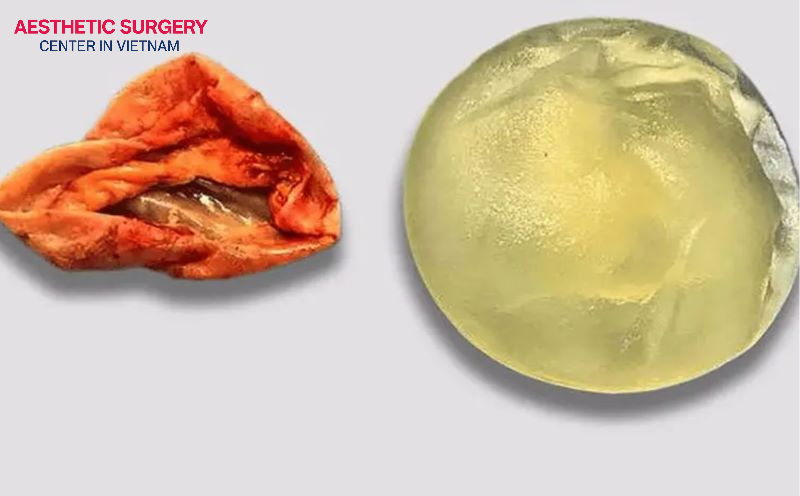
Although modern breast implants are highly durable, the risk of rupture can still occur after several years of use or due to significant trauma. For patients with saline implants, a rupture will cause the implant to deflate, and the saline solution is safely absorbed by the body.
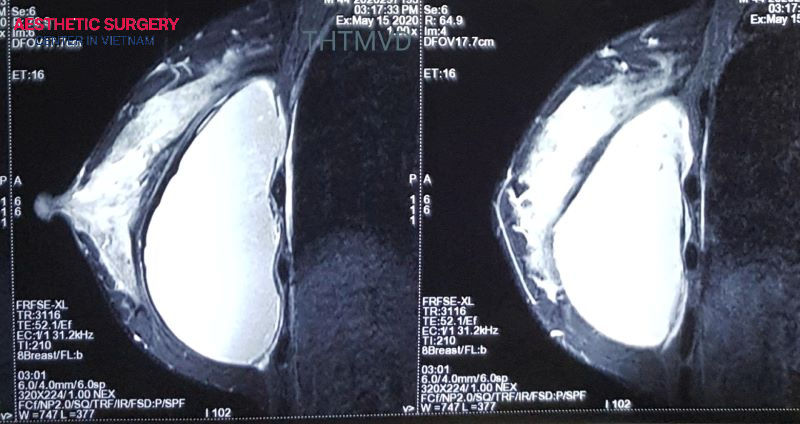
However, for patients with modern cohesive silicone implants, a rupture may leak silently without visible external signs. Therefore, to detect potential issues, patients should undergo regular monitoring with MRI or ultrasound starting 5–6 years after implantation.
Infection and drug reactions
Infections, bleeding, and seroma are potential risks that can occur shortly after breast augmentation surgery. Surgeons should carefully assess patients for any risks beforehand and provide detailed post-operative care instructions to prevent these complications.
If a patient experiences severe or prolonged pain, or develops a serious infection, it may be necessary to remove the implant for thorough treatment before considering re-implantation.
Impact on breastfeeding
Most women can breastfeed after breast augmentation. However, if the implant is placed over the muscle or the incision passes through the areola, it may damage the milk ducts and reduce milk production. This depends on the specifics of the surgical plan, including the incision location chosen by the surgeon.
If you wish to breastfeed after surgery, discuss your needs and the surgeon’s technique in detail to understand whether it may affect you.
Lymphoma
Rare studies have indicated a potential link between textured breast implants and Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). Although the risk of developing this type of lymphoma is very low, patients should receive thorough counseling before choosing the type of implant. BIA-ALCL typically appears as a breast lump and unexplained swelling, often occurring several years after the initial implant placement.

Temporary loss of sensation
After breast augmentation, sensitivity in the nipples and breast area may change, either increasing or decreasing, and can include mild pain or tingling. In most cases, sensation returns to normal within a few months. However, in rare instances, some patients may experience permanent changes in sensation.
Mild keloid formation
For individuals prone to keloid scarring, the incision after breast augmentation may leave raised or darkened scars, especially if exposed to sunlight too soon. Patients should follow post-operative care instructions, avoid strenuous activity, and may use silicone sheets once the wound has healed.
If the breast augmentation scars affect aesthetics, treatments such as steroid injections, microneedling, or laser therapy can help fade and improve the scar’s appearance.
Factors that increase the risk of complications in breast augmentation
Besides individual physiology, certain factors related to implant materials, overall health, and surgical technique can increase the risk of complications after breast augmentation, including:
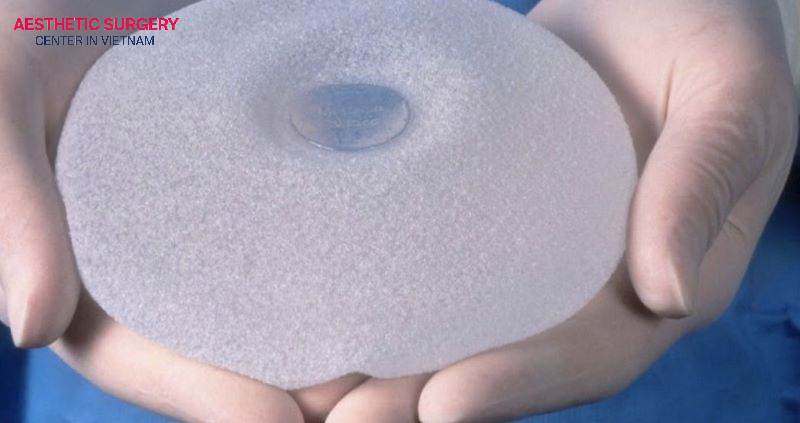
- Implant material: The quality and type of breast implant directly affect safety and longevity. Low-quality or unverified implants may lead to leakage, rupture, or capsular contracture.
- Skin condition: Patients with thin skin or minimal breast tissue may have difficulty covering the implant, increasing the risk of rippling or deformity.
- Overall health: Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or blood clotting disorders can increase the risk of infection and prolong wound healing.
- Surgical technique and surgeon skill: The surgeon’s experience and adherence to proper procedures are crucial in minimizing risks. An experienced surgeon will select the appropriate implant size and placement to ensure both safety and optimal aesthetic results.

>>>See more: breast augmentation questions
Ways to minimize risks in breast augmentation
Although breast augmentation carries certain risks, patients can actively reduce complications by making careful choices and following their surgeon’s instructions. Below are important steps to help minimize risks during breast augmentation:
Understand the longevity and quality of implant materials
Patients should choose FDA- or CE-certified implants to ensure quality and safety. For implants with a lifespan of 10–20 years or more, patients should also consider the potential cost of replacement in the future. Additionally, the surgeon will advise on whether smooth or textured implants are better suited to the patient’s individual anatomy.
Choose a reputable clinic or hospital for breast augmentation
Selecting the right surgical facility plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and success of breast augmentation, while also reducing the risk of unwanted complications. Aesthetics Surgery Center is one of the reputable centers in Vietnam, featuring a team of experienced doctors, modern equipment, and standardized medical care procedures. This helps patients minimize risks and achieve natural, long-lasting results.
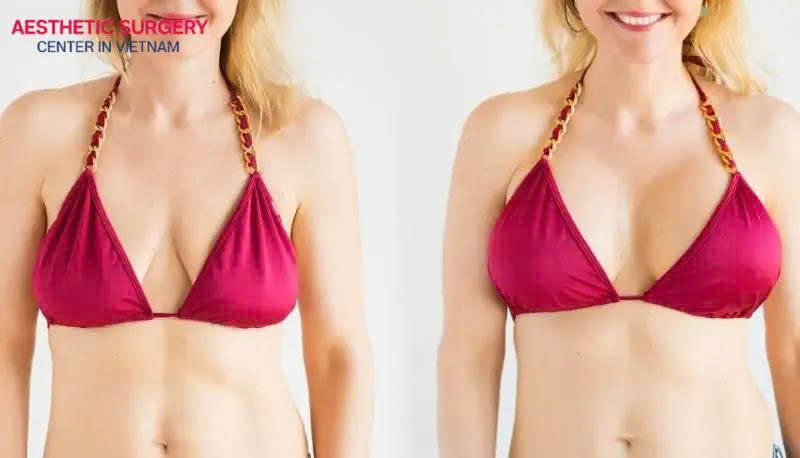

Postpone pregnancy or breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or planning to breastfeed, patients should wait at least six months after giving birth to allow the body to fully recover. This helps the incision heal properly, reduces the risk of infection, and minimizes impact on milk production.
Regular MRI/X-ray screening
Before breast augmentation, patients should undergo X-ray or ultrasound to assess breast tissue health and rule out conditions such as cysts or infections. After silicone implant surgery, doctors typically recommend periodic MRI scans every 2–3 years to detect silent leaks or implant ruptures early, allowing timely intervention.
Care and follow-up after breast augmentation
Post-operative care is crucial after breast augmentation. Patients should rest properly, avoid strenuous activity, refrain from lying on their stomach, and avoid lifting heavy objects for at least the first 4–6 weeks. Additionally, follow the incision care instructions and attend scheduled follow-up visits so the surgeon can monitor the implants and detect any complications early.
Through this article, we hope you now understand the breast augmentation risks and the factors that can increase the likelihood of complications. While breast augmentation is a common procedure, it is generally safe. If you are looking for a reputable clinic, Aesthetics Surgery Center is a strong option. They provide safe, aesthetically pleasing breast augmentation with minimal risk of complications.


























Comment on the post