After a hair transplant, many people experience mild swelling on the forehead or around the eyes overnight. This is a normal reaction of the body to the procedure, but it can still cause concern. Learn why hair transplant swelling occurs, whether it is dangerous, and practical tips to manage it for a smooth recovery.
Causes of hair transplant swelling
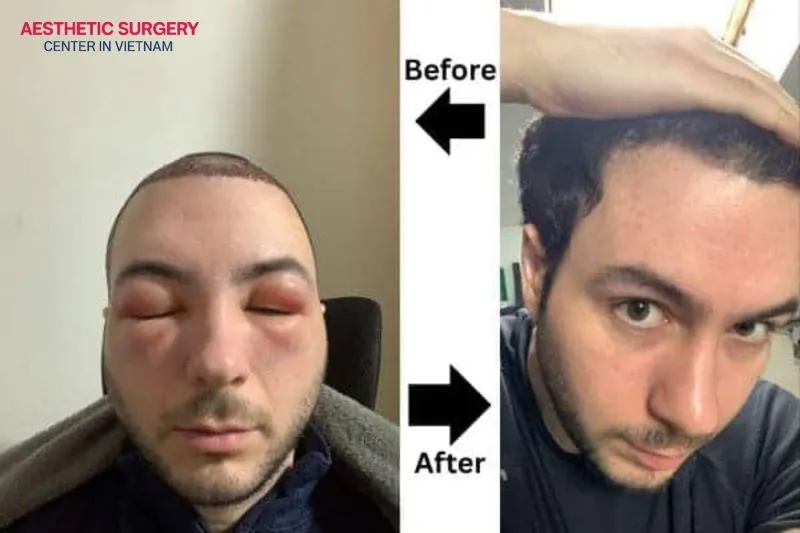
Hair transplant swelling is a common recovery reaction of the body and takes time to subside. This swelling or edema can appear not only at the transplant site but may also spread to the forehead or eyelids. While this is one of the more typical hair transplant side effects, it can cause concern for many patients during the first few days.
Here are some factors that directly affect hair transplant swelling for your reference:
- Mild inflammation: During a hair transplant, the scalp undergoes significant manipulation as the surgeon extracts follicles and creates new graft sites. This can cause minor tissue inflammation, leading to swelling in the first few days, which is a completely natural response of the body.
- Fluid accumulation under the skin: After surgery, tissue fluid and the temporary anesthetic solution can gather under the skin. Due to gravity, this fluid may move toward the forehead or eyelids, making these areas appear slightly swollen and heavier in the first few days.
- Individual sensitivity: People who are more sensitive may experience more swelling, while others may have only mild swelling even if the procedure and recovery process are the same. This depends on factors like water retention, inflammation response, and individual healing speed.
- Transplant technique: If the surgeon performs the procedure gently and precisely, tissue damage is minimal, resulting in less swelling and faster recovery. Conversely, rough handling or excessive pressure on the tissue can trigger a stronger body reaction, causing more swelling after a hair transplant.
Is hair transplant swelling dangerous?
Usually, swelling after a hair transplant is not a dangerous sign. It is a natural response of the body after the scalp tissue has undergone surgery and needs time to heal. In most cases, the swelling gradually decreases within 3–5 days and disappears completely.
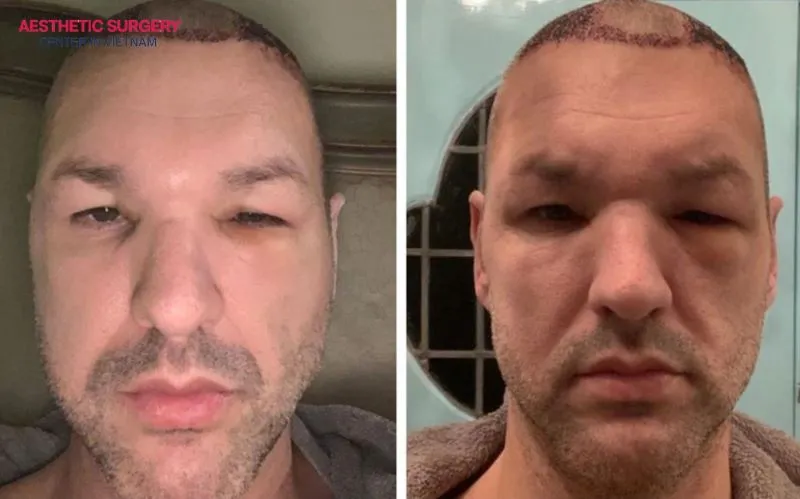
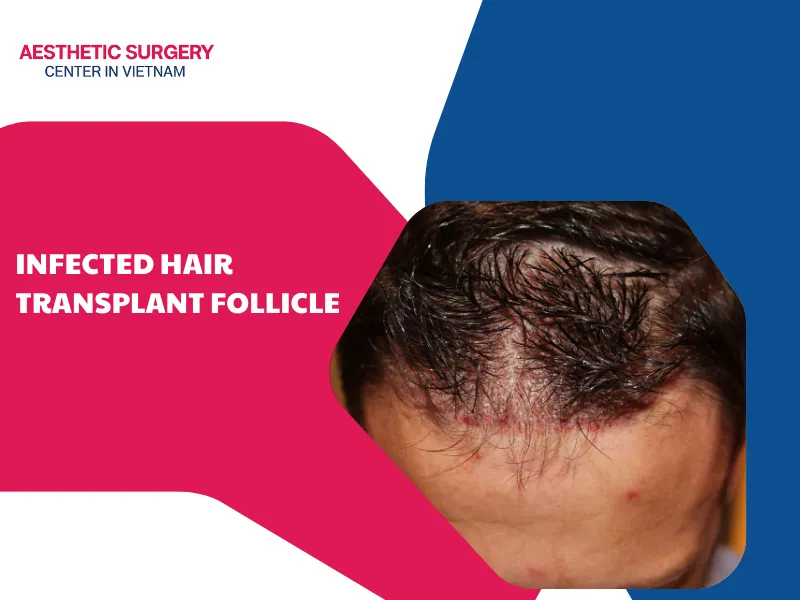
However, there are some red flags you should watch for to ensure your procedure hasn’t become a hair transplant gone wrong. If the swelling is accompanied by increasing pain, a hot or burning scalp, or discharge with a strange odor, it may indicate a serious infection or improper fluid accumulation. In this case, you should contact your surgeon promptly for an emergency examination and timely intervention to protect your results.
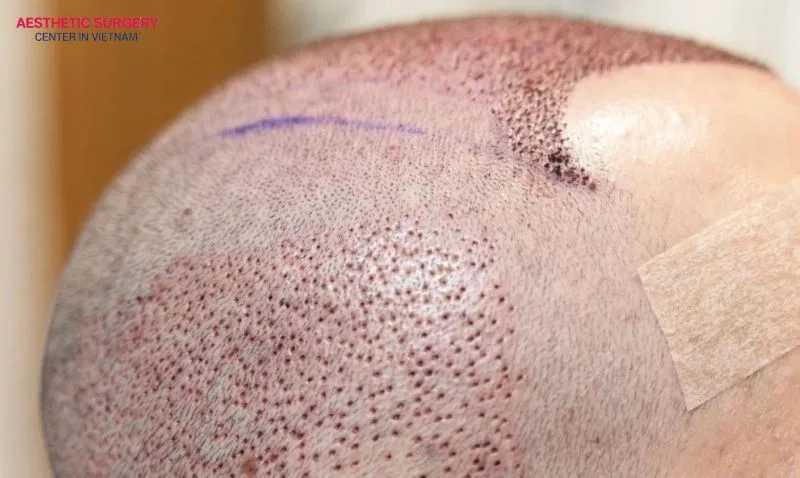
Tips to reduce swelling after a hair transplant
To help swelling subside quickly and speed up hair transplant recovery, you can follow these simple tips:
- Elevate your head while sleeping: In the first few days after a hair transplant, try to keep your head higher than usual, even when resting. Adding 2–3 extra pillows or lying on a reclined chair can prevent fluid from moving down to the forehead and eyelids due to gravity.
- Avoid strenuous activities: Limit activities that raise your heart rate or increase blood flow to the scalp, such as gym workouts, running, or lifting heavy objects. Intense movement can irritate the newly transplanted tissue, prolong swelling and pain, and cause discomfort.
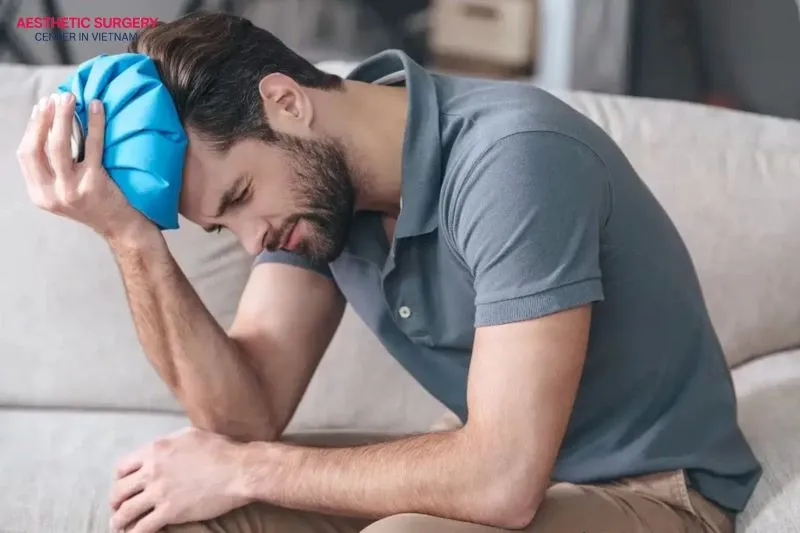
- Apply cold compresses: Gently apply cold packs to areas like the forehead or around the eyes, but never place ice directly on the transplanted scalp. Each session should last 10–15 minutes and can be repeated several times a day to reduce swelling and provide relief.
- Medication: Follow your surgeon’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and timing. Do not increase doses, change medications, or use additional drugs without guidance. If you notice unusual symptoms like dizziness, nausea, or rashes, contact your surgeon immediately.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water daily helps your body reduce swelling by flushing out tissue fluid and toxins, supporting smooth circulation and faster recovery, keeping you comfortable in the first days.
- Limit salt intake: Reduce salt in your daily meals, as excessive salt can cause fluid retention and prolong swelling. Opt for lighter meals and a low-sodium diet for the first 5–7 days to support fluid drainage.
- Follow post-operative care instructions: Your surgeon will provide detailed post-surgery care instructions tailored to your procedure. Following them properly will help your scalp recover quickly and minimize swelling and inflammation.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups allow your surgeon to monitor recovery, detect early signs of complications like swelling, redness, or fluid accumulation, and adjust care if necessary.

How to prevent hair transplant swelling
To reduce the risk of swelling after a hair transplant, you can take some measures from the early stage. These steps help your body recover more easily and minimize edema:
- Maintain proper head posture: Right after the transplant, avoid bending your head too low to prevent graft displacement. It is also vital to understand how to sleep after hair transplant procedures; for the first few days, you should sleep on your back with your head elevated and avoid sleeping on your side. Furthermore, habits like looking at your phone for long periods with your head bent can cause tissue fluid to accumulate in the forehead and eyes, leading to increased swelling.
- Use a forehead compression band: Some reputable clinics provide a specialized compression band to wrap gently around the forehead. The pressure from the band helps limit fluid buildup and reduces hair transplant risks of swelling spreading to the eyes.
- Anti-inflammatory medication: In some cases, your surgeon may prescribe a low-dose steroid anti-inflammatory before or after the transplant. This medication reduces tissue inflammation and helps prevent post-transplant swelling.

From the article above, we hope you now understand why hair transplant swelling occurs and know how to care for and prevent it early to ensure a smooth recovery. Additionally, maintain regular self-care habits and always consult your surgeon if you notice any unusual signs.




























Comment on the post